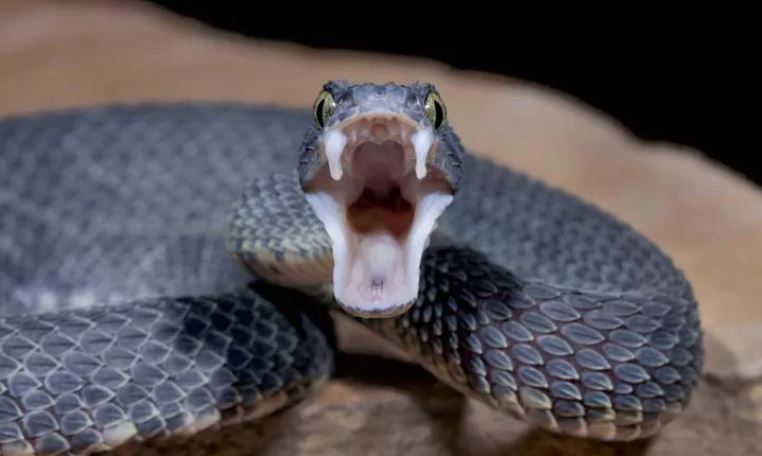
Treatments For Snake Bites You Should Know
How To Treat and Prevent Snake Bite
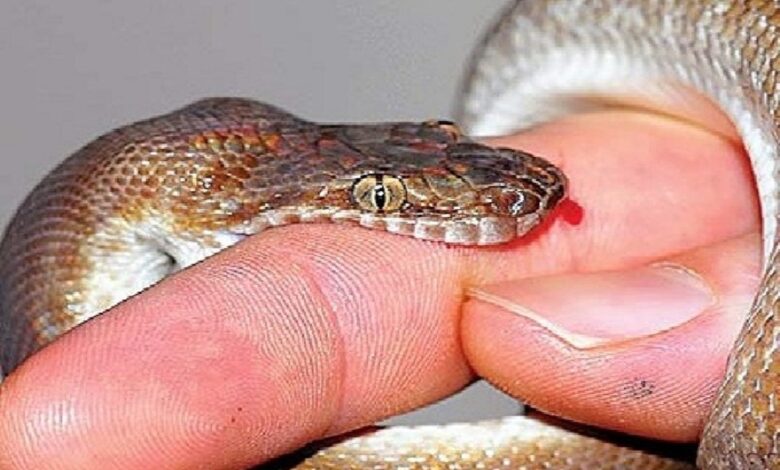

Table of Contents
Snake Bites
What are the symptoms of a snake bite?
If you’re bitten by a snake, your symptoms will differ depending on which type of bite it is. If you suffer a dry snake bite, you’ll likely just have swelling and redness around the area of the bite. But if you’re bitten by a venomous snake, you’ll have more widespread symptoms, which commonly include:
- Bite marks on your skin. These can be puncture wounds or smaller, less recognizable marks.
- Sharp, throbbing, burning pain around the bite that you may not feel for a little while after the bite. You may also feel pain all the way up whichever limb was affected, such as in the groin for a bite on the leg or the armpit for a bite on the arm. But not everyone feels pain. For example, a bite from a coral snake can be almost painless at first, but still deadly.
- Redness, swelling and tissue damage, or complete destruction, in the area of the bite.
- Abnormal blood clotting and bleeding. Severe bleeding can lead to a hemorrhage or kidney failure.
- Low blood pressure, a faster heart rate and a weaker pulse.
- Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, headaches, dizziness and blurred vision.
- Difficulty breathing, or in serious cases, complete loss of breath.
- Increased production of saliva and sweat.
- Weakness in your muscles and numbness in the face or limbs.
If you have an allergic reaction to a snake bite, you could suffer from anaphylactic shock. Many of the symptoms are the same or very similar to the ones listed above, but more severe. But there are a few additional symptoms, including:
- Difficulty speaking due to extreme tightness in the throat and a swollen tongue.
- Young children may become very pale.
- Constant cough and/or wheezing.
First aid myths
There are also several outdated first aid techniques that are now believed to be unhelpful or even harmful:
- Do not use a tourniquet.
- Do not cut into the snake bite.
- Do not use a cold compress on the bite.
- Do not give the person any medications unless directed by a doctor.
- Do not raise the area of the bite above the victim’s heart.
- Do not attempt to suck the venom out by mouth.
- Do not use a pump suction device. These devices were formerly recommended for pumping out snake venom, but it’s now believed that they are more likely to do harm than good.
Treatment for snake bites
The most important thing to do for a snake bite is to get emergency medical help as soon as possible. A doctor will evaluate the victim to decide on a specific course of treatment. In some cases, a bite from a venomous snake is not life-threatening.
The severity depends on the location of the bite and the age and health of the victim. If the bite is not serious, the doctor may simply clean the wound and give the victim a tetanus vaccine.
If the situation is life threatening, the doctor may administer antivenom. This is a substance created with snake venom to counter the snake bite symptoms. It’s injected into the victim. The sooner the antivenom is used, the more effective it will be.
Outlook for a snake bite
The outlook for a person with a snake bite is highly variable. For a non-venomous snake bite, the outlook is excellent if the wound is cleaned and treated promptly. For a venomous bite, the outlook is good if the victim receives emergency care very soon after the bite has occurred.
Healthy adults with shallow bites have a better outlook than children and those with weakened immune systems who have received deep bites.
Prevention of snake bites
Snake bites can be prevented in many cases. It’s best to refrain from approaching or handling snakes in the wild. Avoid typical places where snakes like to hide, such as patches of tall grass and piled leaves, and rock and woodpiles.
If you encounter a snake, give it space to retreat and let it take cover. It’s in the snake’s nature to avoid interaction.
When working outside where snakes may be present, wear tall boots, long pants, and leather gloves. Avoid working outside during the night and in warmer weather, which is when snakes are most active.
For any important information please contact us Email GadgetsNg info@gadgetsng.com
[Button id="1"]