What You Need To Know About COMA
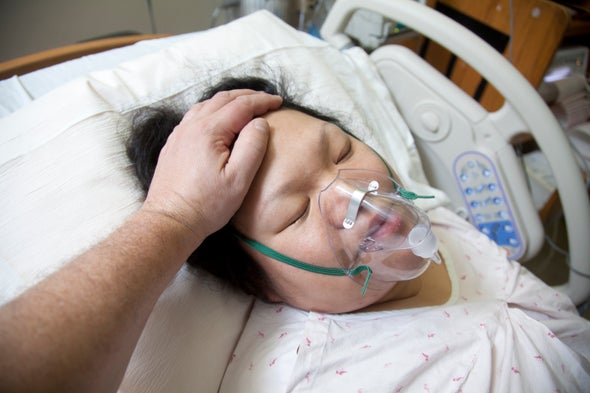
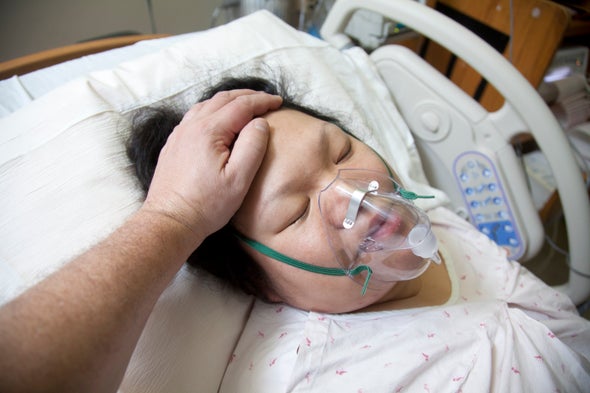
A coma is a prolonged state of unconsciousness. During a coma, a person is unresponsive to his or her environment. The person is alive and looks like he or she is sleeping. However, unlike in a deep sleep, the person cannot be awakened by any stimulation, including pain.
Swift action is needed to preserve life and brain function. Doctors normally order a battery of blood tests and a brain CT scan to try to determine what’s causing the coma so that proper treatment can begin.
A coma seldom lasts longer than several weeks. People who are unconscious for a longer period of time may transition to a persistent vegetative state.
Depending on the cause of a coma, people who are in a persistent vegetative state for more than one year are extremely unlikely to awaken.
Table of Contents
Causes Of Coma
Anoxic brain injury
This is a brain condition caused by total lack of oxygen to the brain. Lack of oxygen for a few minutes causes cell death to brain tissues.
Anoxic brain injury may result from heart attack (cardiac arrest), head injury or trauma, drowning, drug overdose, or poisoning.
Trauma
Head injuries can cause the brain to swell and/or bleed.
When the brain swells as a result of trauma, the fluid pushes up against the skull. The swelling may eventually cause the brain to push down on the brain stem, which can damage the RAS (Reticular Activating System) a part of the brain that’s responsible for arousal and awareness.
Swelling
Swelling of brain tissue can occur even without distress. Sometimes a lack of oxygen, electrolyte imbalance, or hormones can cause swelling.
Bleeding
Bleeding in the layers of the brain may cause coma due to swelling and compression on the injured side of the brain. This compression causes the brain to shift, causing damage to the brainstem and the RAS (mentioned above). High blood pressure, cerebral aneurysms, and tumors are non-traumatic causes of bleeding in the brain.
Stroke
When there is no blood flow to a major part of the brain stem or loss of blood accompanied with swelling, coma can occur.
Blood sugar
In people with diabetes, coma can occur when blood sugar levels stay very high. That’s a condition known as hyperglycemia. Hypoglycemia, or blood sugar that’s too low, can also lead to a coma. This type of coma is usually reversible once the blood sugar is corrected. However, prolonged hypoglycemia can lead to permanent brain damage and persistent coma.
Oxygen deprivation
Oxygen is essential for brain function. Cardiac arrest causes a sudden cutoff of blood flow and oxygen to the brain, called hypoxia or anoxia. After cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), survivors of cardiac arrest are often in comas. Oxygen deprivation can also occur with drowning or choking.
Infection
Infections of the central nervous system, such as meningitis or encephalitis, can also cause coma.
Toxins
Substances that are normally found in the body can accumulate to toxic levels if the body fails to dispose of them correctly. As an example, ammonia due to liver disease, carbon dioxide from a severe asthma attack, or urea from kidney failure can accumulate to toxic levels in the body. Drugs and alcohol in large quantities can also disrupt neuron functioning in the brain.
Seizures
A single seizure rarely produces coma. But continuous seizures — called status epilepticus — can. Repeated seizures can prevent the brain from recovering in between seizures. This will cause prolonged unconsciousness and coma.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a coma commonly include:
- Closed eyes
- Depressed brainstem reflexes, such as pupils not responding to light
- No responses of limbs, except for reflex movements
- No response to painful stimuli, except for reflex movements
- Irregular breathing
How To Take Care of Someone in a Coma
Someone in a coma usually needs to be cared for in the intensive care unit (ICU) of the hospital. There, the person can get extra care and attention from doctors, nurses, and other hospital staff. They make sure the person gets fluids, nutrients, and any medicines needed to keep the body as healthy as possible. These are sometimes given through a tiny plastic tube inserted in a vein or through a feeding tube that brings fluids and nutrients directly to the stomach.
Some comatose people are unable to breathe on their own and need the help of a ventilator (say: VEN-tih-lay-ter), a machine that pumps air into the lungs through a tube placed in the windpipe. The hospital staff also tries to prevent bedsores in someone who is comatose. Bedsores are open sores on the body that come from lying in one place for too long without moving at all.
It can be very upsetting and frustrating for a person’s family to see someone they love in a coma, and they may feel scared and helpless. But they can help take care of the person. Taking time to visit the hospital and read to, talk to, and even play music for the patient are important because it’s possible that the person may be able to hear what’s going on, even if he or she can’t respond.
For any important information please contact us Email GadgetsNg info@gadgetsng.com
[Button id="1"]



e08hag