
Table of Contents
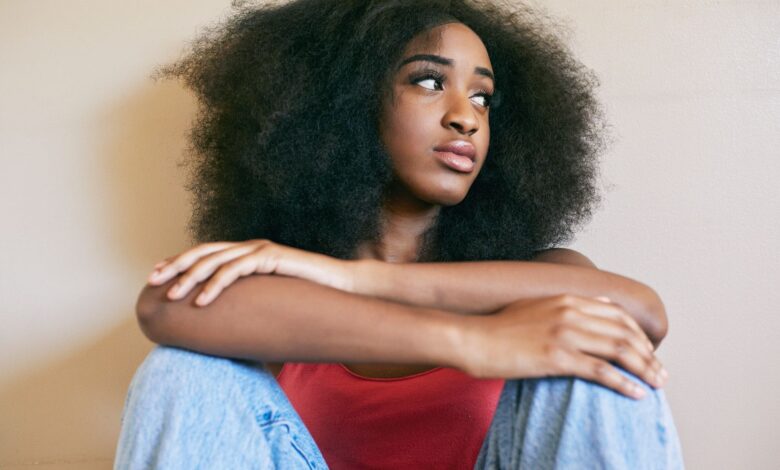
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
Abnormal vaginal bleeding occurs between menstrual periods, after sex, or after menopause. Menstrual periods that are heavier or last longer than usual or last more than seven days also are considered abnormal.
Your doctor will likely perform a physical and pelvic exam and may test your blood, hormone levels and thyroid function to determine if you are pregnant or infected with a sexually transmitted disease.
Imaging tests such as pelvic ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound, ultrasound of the uterus, pelvic MRI, hysteroscopy or endometrial biopsy also may be used to help diagnose your condition.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include medication, uterine fibroid e-mobolization, endometrial ablation or surgical intervention.
A range of causes
In many women, the cause of the irregular bleeding is not found. For others, the cause depends on their age and the site of bleeding. Once pregnancy has been ruled out, some of the known causes include:
- Hormonal changes
- Contraception such as the pill, injection or IUD (intrauterine device)
- Infection in the vagina or uterus
- Fibroids or polyps inside the uterus
- Trauma to the vagina
- Some medications such as anticoagulants or anti-epilepsy drugs
- Underlying health problems such as bleeding or thyroid disorders
- Cancer in the lining of the uterus, the cervix or vagina (rare).
When to seek medical help
You should consult your doctor any time you have abnormal vaginal bleeding. The cause of the bleeding could be serious and should be determined. See your doctor right away if you’re pregnant and have vaginal bleeding.
If you have other serious symptoms in addition to bleeding, you may need emergency medical attention. These include:
- pain
- fatigue
- dizziness
- fever
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for vaginal bleeding between periods. Treatment will vary based on what’s causing your abnormal vaginal bleeding.
For any important information please contact us Email GadgetsNg info@gadgetsng.com
[Button id="1"]




nxediyunlandayi.h5I5SKeWA2fv
xyandanxvurulmus.IpJY3jNueuTr
xbunedirloooo.x5NSvZyxiSpe
misreferred xyandanxvurulmus.sadwLgmuyj48
anal siteleri citixx.J3Lxu2EgaquT
seksi siteler wrtgdfgdfgdqq.vSfBlizCBPMQ
Ücretsiz Canli Seks Sohbet XXX Kameraları Genc Seksi Kizlar
childrens sex pompadirha.s8xm4j3EOz1O
bahis siteleri sikis asillartaklitler.ZQ5NANpX6HW6
childrens sex hephupx.ORWjF0oUkzd7
bahis porno hepxhupx.pnLxga1vLQ9Z
sohbet.net sohbet sikesinde sikis filmleri izleyebilirsiniz porno film cevirebilirsiniz
grandpashabet, grandpashabet giriş, grandpashabet bonus
KahveOyun.com – Mobil ve bilgisayar üzerinden okey odalarında oynayarak zaman geçireceğiniz ve okey oynarken sohbet edebilme fırsatını ücretsiz sunmaktadır.
porn k hd gghkyogg.2tt2hdRpCCg
hd sex video download 4k ggjennifegg.GP1E9kGWrMH
Kahve amina Okey ayagimi Kahvesokucamokey
goodhere Funny Sex porn vurucutewet.oSsDw2bNqPW
ladyandtherose Vintage porn backlinkseox.yC5YV51vlJh
jenniferroy 毛深いポルノ japanesexxporns.qouqgXz5fx0
landuse Big Tits porn lancdcuse.QtvmhrnQkgQ
falbobrospizzamadison Man Masturbating porn jkkıjxxx.vtff4kBM5FI
बृहत् गधा अश्लील qqyyooppxx.N2eYSgOqINB
छोट-छोट स्तन अश्लील hjkvbasdfzxzz.kVxEPfo0C5X
o bizden caldigin tasarimlari ananin amina sokucaz az kaldi bekle
बालों वाली अश्लीलता txechdyzxca.Cjy4jxBU9iz
परिपक्व(40 ) पोर्न hkyonet.GoCxBaFJ9GH
ਕਾਰਟੂਨ ਪੋਰਨੋਗ੍ਰਾਫੀ madisonivysex.yAz5Bq2cYq9
ladesbet ਲਿੰਗੀ ਪੋਰਨ ladesinemi.P1hxVeWvlBP
ladesbet レズビアンのポルノ ladestinemi.1lvtcjtgJZm
sitenizi takip ediyorum makaleler Faydalı bilgiler için teşekkürler